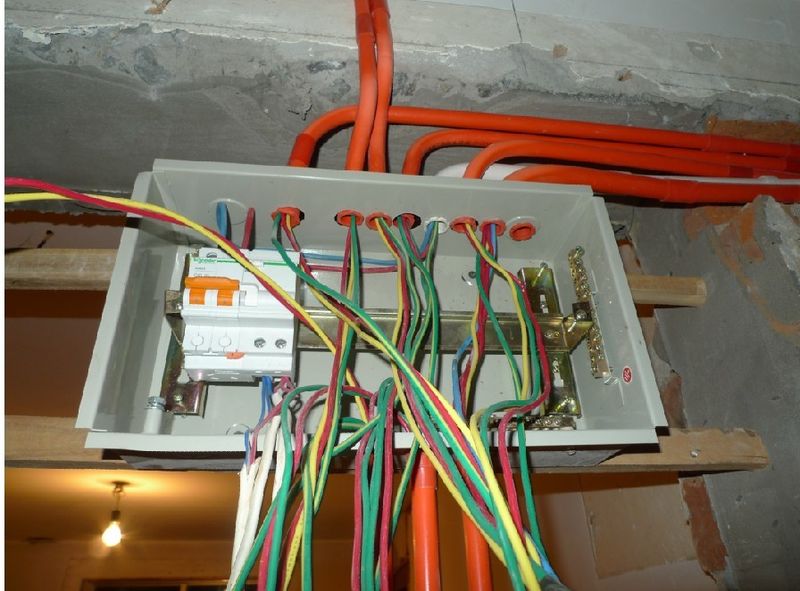
1. Concept and characteristics: the essential difference between energy transmission and information carrier The fundamental difference between strong and weak electricity lies not only in the voltage value, but also in the physical characteristics and functional positioning. The strong power system is mainly 220V/380V AC, with a fixed frequency of 50Hz, and its core function is transmitting […]
1. Only look at price and ignore quality: low-price traps hide safety hazards In the purchase of wires, price is often the most intuitive decision-making factor for consumers. However, according to the 2023 spot check data of the State Administration for Market Regulation, the qualified rate of low-priced wires is only 67.3%, significantly lower than […]
1. The essential difference in fire prevention mechanisms The core mission of flame-retardant cables: “firewalls” that prevent flames from spreading along cables The secret of flame-retardant cables lies in their special material formula. When encountering flames, the flame retardant in its sheath self-extinguishes through the halogen flame retardant effect or the precipitation of water vapor […]
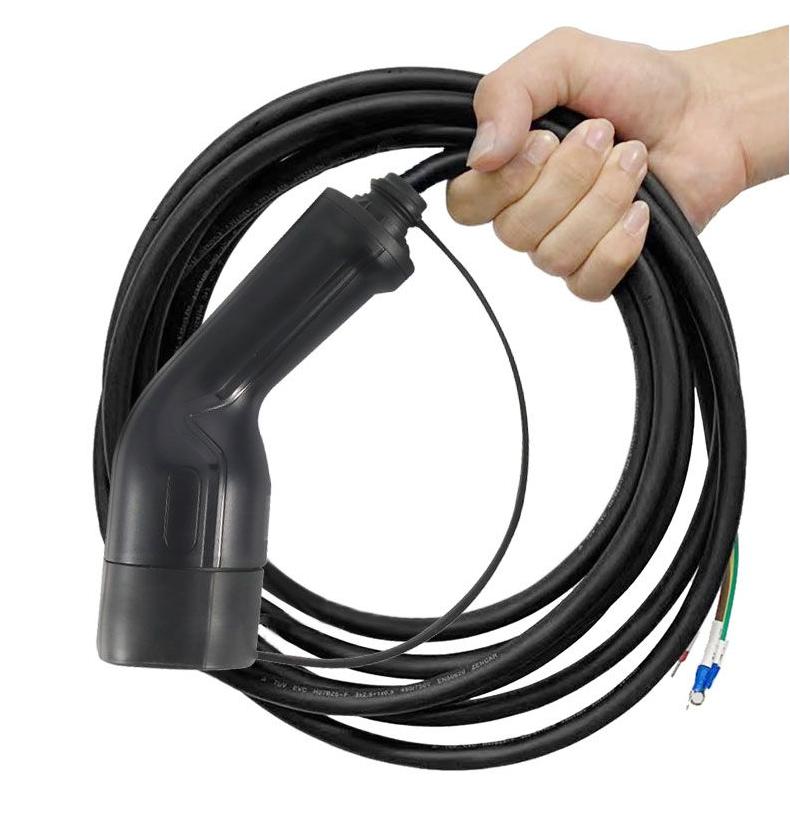
1. Functional integration: intelligent carrier beyond energy transmission Modern charging cables are no longer simple power channels. In order to achieve real-time interaction and safe control of the battery status of charging piles and vehicles (such as adjusting current and monitoring insulation), cables must integrate communication and control cores. For example, the typical structure of […]
1. Accurate calculation and dynamic planning of current load According to the IEC 60287 standard, the cross-sectional area of the conductor must meet the dual requirements of current carrying capacity and thermal stability. Taking an industrial park project as an example, the peak current is calculated to be 385A by the dynamic load prediction method. […]
1. National standard 0.6mm threshold: scientifically verified safety baseline GB/T 5013-2008 “Rubber insulated cables with rated voltages of 450/750V and below” clearly stipulates that the nominal insulation thickness of rubber-sheathed cables shall not be less than 0.6mm. Behind this seemingly simple value is the verification result of Tsinghua University’s high voltage laboratory over a period […]
1. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): A model of economical insulation As an insulating material with a global usage of 38% (data source: Grand View Research 2023), PVC builds a safety line of defense for low-voltage electrical systems with its excellent cost-effectiveness. Its volume resistivity can reach 1×10¹²Ω·m, and with a rated voltage range of 0.6-1kV, it […]
1. Material game of conductors: technical choices behind the copper-aluminum dispute In terms of conductor selection, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC 60228 standard) clearly stipulates that rubber-sheathed cable conductors must meet the technical requirements of DC resistance not exceeding 17.241Ω/km at 20°C. The 2022 Cable Industry Report of the U.S. Department of Energy shows that […]
1. Composition and material innovation of rubber-plastic cables The basic structure of rubber-plastic cables consists of four parts: conductor, insulation layer, shielding layer and sheath (Figure 1). Among them, the choice of insulating material directly determines the upper limit of the performance of the cable. For example, cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) is widely used in medium and high […]
1. Power cable technology innovation: the core engine supporting energy transformation With the rapid development of UHV power grids and new energy power generation, power cables are upgrading to high voltage, large capacity and intelligence. For example, domestic ultra-high voltage cables have broken through the key technology of 500kV and have been applied on a […]